- Guides & Tools
- Pushed Authorization Requests (PAR)
- Getting Started
- eIDs
- Guides & Tools
- Articles
- Age Verification
- Authorize URL builder
- Caller Authentication with CIBA
- Single Sign-on
- Creating test users
- Work with metadata
- App switching
- Choose language
- Prefilled input fields
- Custom styling
- Private key JWT authentication
- Get ready for production
- Pushed Authorization Requests (PAR)
- Telemetry & observability
- Integrations
- Reference
Guides & Tools
Pushed Authorization Requests (PAR)
Pushed Authorization Requests (PAR) is an OAuth 2.0 extension that allows sending authorization request parameters to the authorization server via a POST request, rather than in the browser's URL query string.
PAR enhances security by mitigating risks associated with exposing sensitive data in URLs. It also allows the authorization server to authenticate the client and validate the request early in the process (before any user interaction occurs), which can prevent attempts to spoof clients or otherwise tamper with or misuse an authorization request.
Using PAR improves Telemetry & Observability for your Idura applications:
it helps you trace authorization requests by giving you a Trace-Id to follow immediately and directly to your backend.
PAR can be used with any OpenID Connect flow that involves authorization requests sent via the browser, including the Authorization Code Flow and the Authorization Code Flow with PKCE.
How PAR works
Regular authorization requests are made by redirecting the user's browser to the OAuth2 authorization endpoint (/oauth2/authorize) with all parameters included in the URL.
The process with PAR is slightly different:
- Your backend makes a POST request containing request parameters (those you would otherwise include in the URL query string) to the PAR endpoint (
/oauth2/par). - The authorization server responds with a
request_uri, a unique identifier for your request. - Your application redirects the user's browser to the authorization server's authorization endpoint, including the
request_uriobtained from the PAR response and the application'sclient_id. - The authorization server retrieves the original request parameters using the
request_uriand proceeds with the authentication flow.
Implementing PAR with Idura
You can start using PAR in place of standard authorization requests by following the steps below.
1: Push the authorization request from your backend
Send a POST request from your backend to the PAR endpoint. The PAR endpoint URL can be found in your
OIDC Discovery Document under pushed_authorization_request_endpoint.
Your POST request should include:
- The same parameters you would normally send in an authorization request (e.g.
response_type,scope,redirect_uri,state). For the complete list of authorization request parameters, see Authorize Request Parameters. - Client authentication credentials (for confidential clients):
- either
client_idandclient_secret(included in the Basic Authorization header) or client_assertionandclient_assertion_type(included in the request body), when using Private Key JWT.
- either
code_challengeandcode_challenge_method(for public clients or clients implementing Authorization Code Flow with PKCE).
The PKCE extension to the Authorization Code Flow is required for public clients and recommended for confidential clients. It offers stronger protection against the misuse or injection of authorization codes, making your implementation more secure.
For more details, see OpenID Connect best security practices.
Example PAR Request (Basic Auth):
# Replace `YOUR_DOMAIN.idura.broker` with your Idura domain
# Replace `$client_id` and `$client_secret` with the client credentials of your Idura Application
# Replace `$your_return_url` with the redirect URI registered in your Idura application
POST https://YOUR_DOMAIN.idura.broker/oauth2/par HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Basic $base64_$client_id:$client_secret
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
client_id=$client_id&
response_type=code&
scope=openid%20profile&
redirect_uri=$your_return_url&
state=abc456
Example PAR Request (Private Key JWT):
# Replace `YOUR_DOMAIN.idura.broker` with your Idura domain
# Replace $client_id with the Client ID of your Idura Application
# Replace `$client_assertion` with your JWT assertion
# Replace `$your_return_url` with the redirect URI registered in your Idura application
POST https://YOUR_DOMAIN.idura.broker/oauth2/par HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
client_id=$client_id&
client_assertion_type=urn%3Aietf%3Aparams%3Aoauth%3Aclient-assertion-type%3Ajwt-bearer&
client_assertion=$client_assertion&
response_type=code&
scope=openid%20profile&
redirect_uri=$your_return_url&
state=abc456
Example PAR Request (PKCE):
# Replace `YOUR_DOMAIN.idura.broker` with your Idura domain
# Replace $client_id with the Client ID of your Idura Application
# Replace `$your_return_url` with the redirect URI registered in your Idura application
POST https://YOUR_DOMAIN.idura.broker/oauth2/par HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
client_id=$client_id&
code_challenge=E9Melhoa2OwvFrEMTJguCHaoeK1t8URWbuGJSstw-cM&
code_challenge_method=S256&
response_type=code&
scope=openid%20profile&
redirect_uri=$your_return_url&
state=abc456
Successful Response:
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/json
{
"request_uri": "urn:ietf:params:oauth:request_uri:69091cba-850f-4e7d-9c37-b5c6a74e0e02",
"expires_in": 120
}
The response contains:
request_uri: the identifier of the authorization request pushed by the client application.
expires_in: the lifetime of the request_uri in seconds.
2: Redirect the user to the authorization endpoint
After receiving the request_uri, redirect the user's browser to the authorization endpoint. Only client_id and request_uri parameters must be included in the authorization request.
Example Authorization Request:
GET https://{{YOUR_IDURA_DOMAIN}}/oauth2/authorize?client_id=your_idura_application_client_id&request_uri=urn:ietf:params:oauth:request_uri:69091cba-850f-4e7d-9c37-b5c6a74e0e02
The authorization server uses the request_uri to retrieve the original request parameters.
The rest of the authentication flow then proceeds as usual.
3: Enforce PAR (optional)
You can enforce PAR by toggling Require Pushed Authorization Requests (PAR) in your application's OpenID Connect settings in the Idura Dashboard.
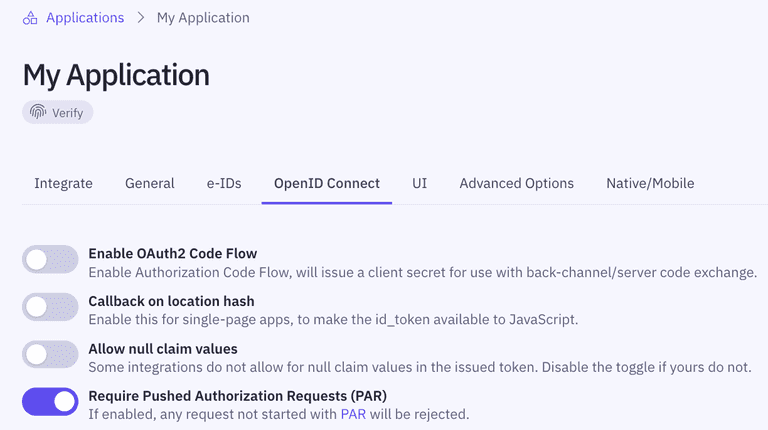
Why enforce PAR?
Enforcing PAR improves security by preventing attackers from starting requests. Otherwise, even if you use PAR yourself, an attacker could still use regular authorization requests.